Shared Nothing
This page contains settings specific for a Shared-Nothing Cluster. The first tab relates to snapshot settings:
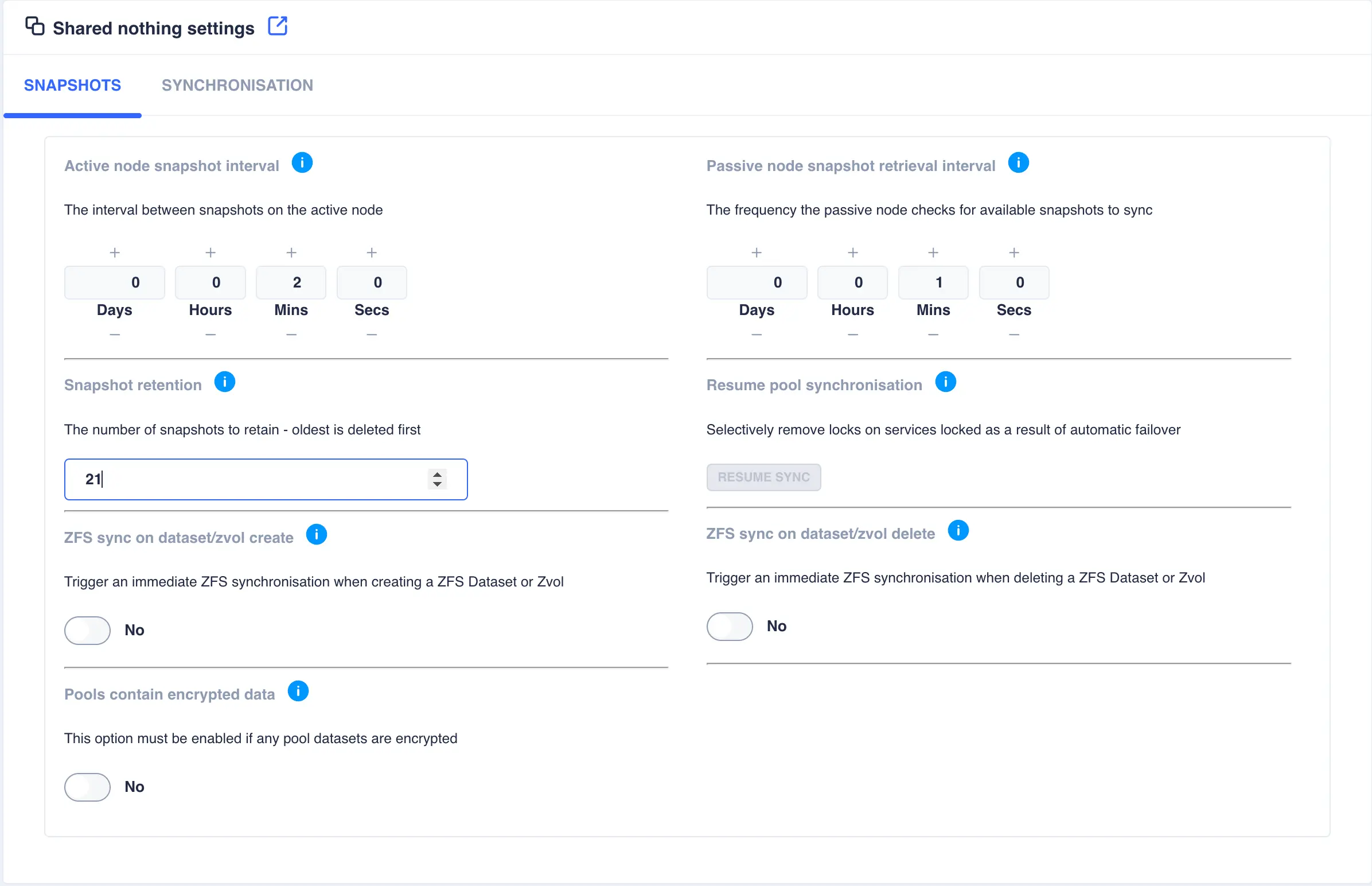
Setting |
Description |
|---|---|
Active node snapshot interval |
Sets the frequency by which snapshots are taken of a pool on its active node. The passive node is responsible for replicating these snapshots using ZFS send/receive. The amount of snapshots kept locally is governed by the snapshot retention value. |
Passive node snapshot retrieval interval |
Sets the frequency by which the passive node checks an active node to ensure it has up-to-date copies of all active pool snapshots. Any missing snapshots will be synchronised using ZFS send/receive and any expired snapshots (as dictated by the snapshot retention value) will be removed. Using a pull mechanism ensures any node recovering after a crash will immediately synchronize any missing snapshots. Using this approach also removes the requirement for the active node to continually attempt to send snapshots to the passive node, which could be unavailable. |
Snapshot Retention |
The amount of snapshots to be retained for each pool on all nodes. Once the retention number is reached, and as new snapshots are taken, the oldest are purged to maintain the snapshot retention level. |
Resume pool synchronisation |
In the event of an aotomatic failover due to a system failure, once the failed node recovers, synchronisation is suspended to prevent data loss as there maybe existing data that had not yet been synchronised when the node failed - for a more detailed explanation of this scenario please see this description. Once remedial action has been taken click the RESUME SYNC button to resume synchronisation on selectable service basis. |
ZFS sync on dataset/zvol create |
When a dataset/zvol is created it is synchronised over to the other node during the scheduled snapshot/synchronisation cycle. Enabling ZFS sync on dataset/zvol create means that as soon as a dataset/zvol is created a snapshot is taken and a remote synchronisation will be performed, after which the normal synchronisation cycle resumes. |
ZFS sync on dataset/zvol delete |
When a dataset/zvol is deleted, the delete is performed on the remote node as part of the scheduled synchronisation cycle. Enabling ZFS sync on dataset/zvol delete means that when a dataset/zvol is deleted locally, it will also be deleted on the remote node. |
Pools contain encrypted data |
In order to replicate encrypted datasets, it is necessary to transfer data in a raw format; this setting forces the raw option for ZFS send/receive. It is not enabled by default due to a slight overhead when transferring data in a raw format. |
The second tab relates to synchronisation settings:
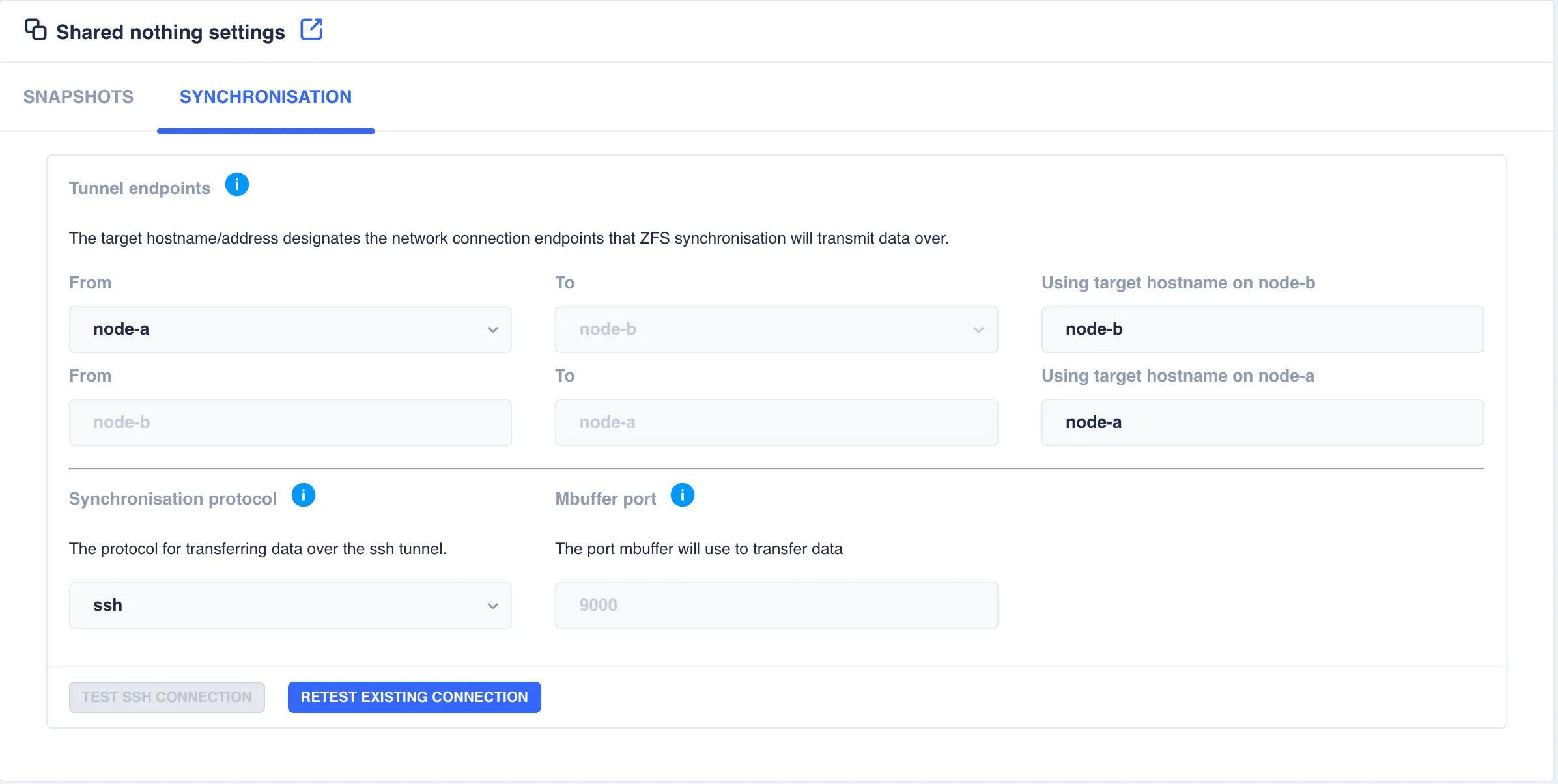
Setting |
Description |
|---|---|
Tunnel endpoints |
In a shared nothing cluster, snapshots are synchronised using a ssh tunnel, which by default uses the interfaces the cluster hostnames are plumbed in on. However, if other channels exist between the two nodes (for example a high-speed private network) then use this option to change which channels the cluster uses to send synchronisation data over. To change channel end points, specify the hostname plumbed in on the remote node for the desired channel, for example if a node has a main interface with hostname node-b and a private interface with hostname node-b-priv then set the end point for node-a to be node-b-priv. Note that this configuration should be done for each channel direction. |
Syncrhonisation protocol |
Select either ssh or mbuffer as the synchronisation protocol. The SSH protocol encrypted data which slows transfer speed down. The mbuffer protocol does not encrypt data, thereby allowing faster transfer speeds. Select the protocol that best suits security needs. |
Mbuffer Port |
By default the mbuffer receiving side process listens on port 9000. This option allows customisation of the listen port; the mbuffer client will automatically connect to the port defined here. |